
서비스분야
현재 위치:홈 > Services & Solutions > Integrated Projects > Rodent Cerebrovascul...
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases generally refer to ischemic or hemorrhagic diseases of the heart, brain and systemic tissues caused by hyperlipidemia, blood viscosity, atherosclerosis, and hypertension.
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases generally refer to ischemic or hemorrhagic diseases of the heart, brain and systemic tissues caused by hyperlipidemia, blood viscosity, atherosclerosis, and hypertension.

|
Disease
|
ICD 10
|
Models
|
| Intracerebral hemorrhage | I60-I62 | Intracranial Autologous Blood Injection,Subarachnoid hemorrhage | |
| Cerebral infarction | I63 | Ischemic stroke model | |
| Stroke | I64 | ||
| Cerebral thrombosis | I65 | ||
| Cerebral Embolism | I66 | ||
| Other | I67-I69 | Other |
The annual treatment cost of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in China is RMB 540.6 billion. The annual treatment cost of cerebrovascular diseases accounts for 25.68% of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Among them, ischemic stroke accounts for 18% and hemorrhagic stroke accounts for 7%.
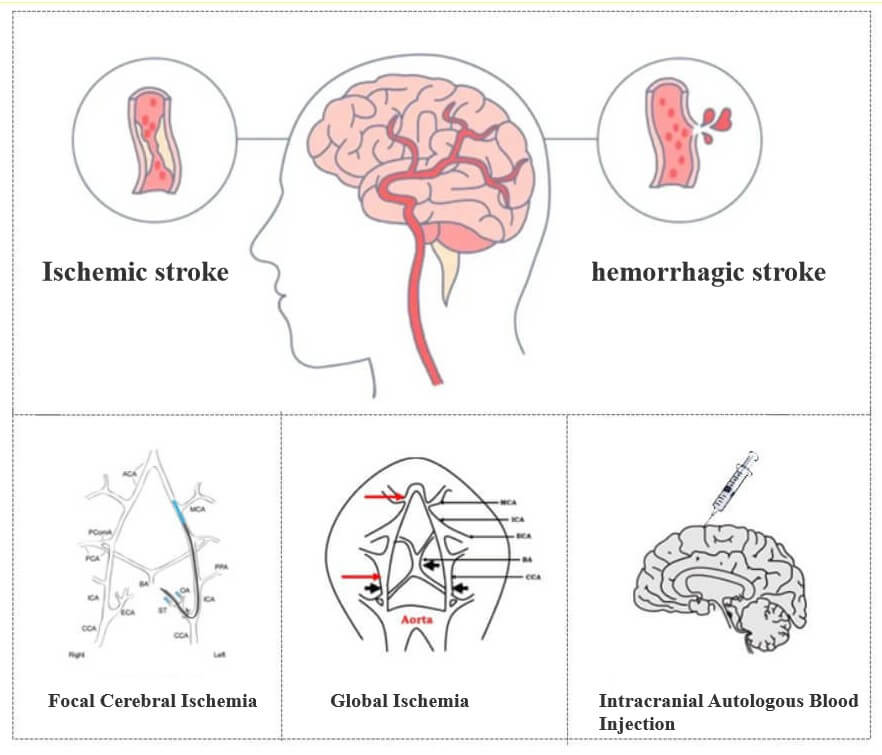
• Rat and mouse MCAO models with stable lesions, high success rate and high survival rate
• Reliable and effective evaluation of dose-effect/time-effect relationship
• Efficacy evaluation of transient cerebral ischemia and permanent cerebral ischemia
• Complete the investigation of various pharmacodynamic core indicators according to STAIR technical guidelines
• The model rodents could be customized with special diseases and complete activity evaluations according to customer requirements
Animals: ICR mice, male
Group: Control Group, Model Group, Positive Drug Group (Xianbixin)
Methodology:
• The right middle artery of the mice was blocked by suture method, and the suture was removed after blocking for 1 h to achieve reperfusion.
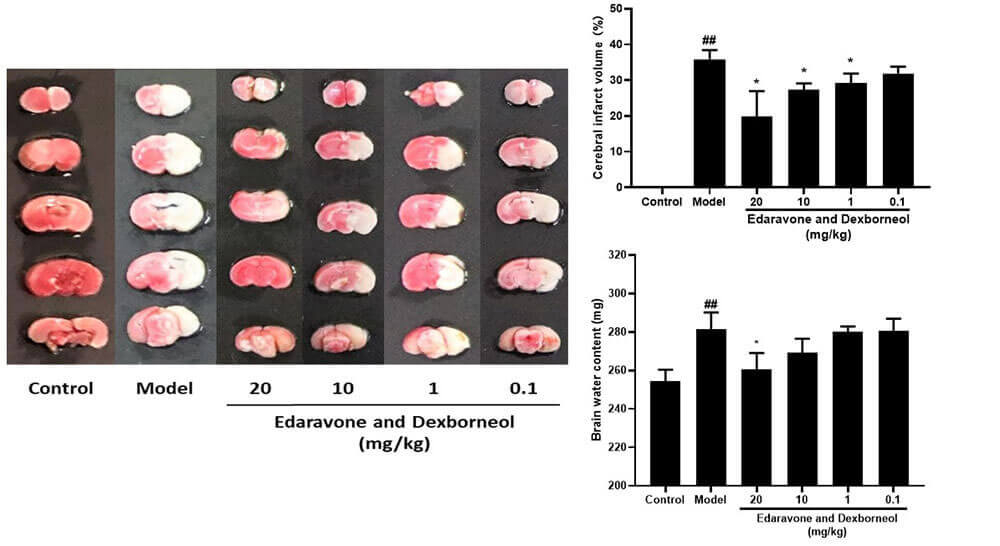
• Dose-Response Investigation: Animals were given the positive drug Xianbisxin 20, 10, 1, 0.1 and 0.01 mg/kg intravenously at 0.5h after infarction, respectively, and the dose-effect relationship was investigated.
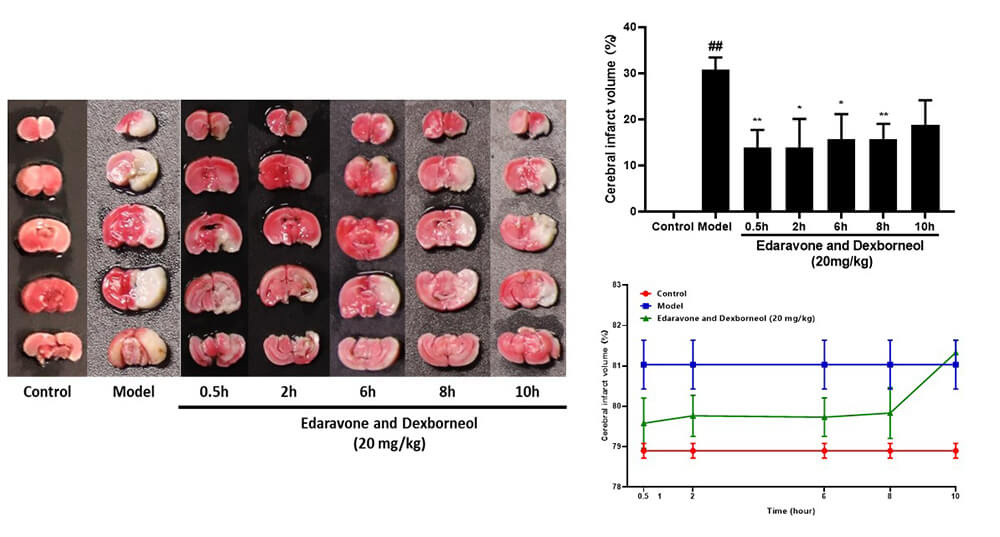
• Time-Response Investigation: Animals were given the positive drug Xianbixin 20mg/kg intravenously at 0.5h after infarction and 2h, 6h, 8h and 10h after reperfusion respectively, and the time-effect relationship was investigated.
Inspection indicators
The infarct volume was measured by TTC method, and the brain water content was measured by drying method.
Dose-Effect Relationship Study (TTC and brain water content) (mean±SEM)
Time-Effect Relationship Study (TTC and brain water content) (mean±SEM)
Animals: ICR mice, male
Group: Control Group, Model Group, Positive Drug Group (Xianbixin)
Methodology:
• The right middle artery of the mice was blocked by suture method, and the suture was removed after 1h, 2h and 4h of blocking to achieve reperfusion.
• Treatment Time Window Investigation: Animals were intravenously injected with the positive drug Xianbixin 20mg/kg 0.5h after infarction, and the treatment time window was investigated.
Inspection indicators
Infarct volume was measured by TTC method, brain volume by drainage method, and brain water content by drying method.
Result
Treatment Time Window Investigation A: TTC; B: Brain Volume, C: Brain Water Content (mean±SEM)

Animals: ICR mice, male
Group: Control Group, Model Group, Positive Drug Group (Xianbixin)
Methodology:
• The right middle artery of the mice was blocked by suture method, and the suture was removed after blocking for 1 h to achieve reperfusion.
• Neurological Recovery Investigation: Animals were intravenously injected with the positive drug Xianbixin 20mg/kg 0.5h after infarction, and the treatment time window was investigated.
Inspection indicators
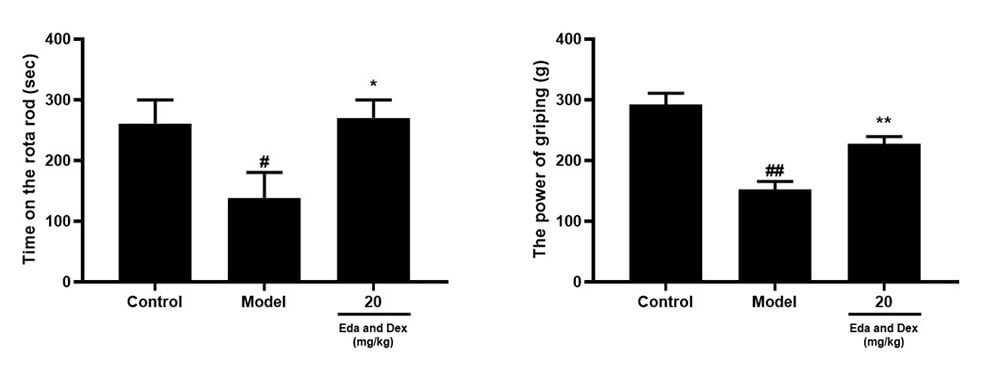
Zea-longa score, Balance Beam Transit Time, Rotarod Dwell Time, Grip Strength
Pharmacodynamic Investigation of Neurological Function: A: Zea-longa score; B: Balance Beam Transit Time
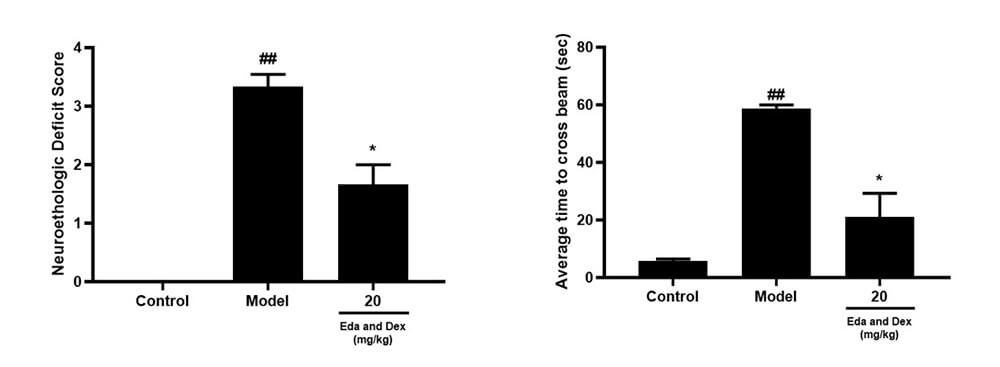
Pharmacodynamic Investigation of Neurological Function: C: Rotarod Dwell Time; D: Grip Strength
Animals: SD Rat, male
Group: Control Group, Model Group, Positive Drug Group 1 (Edaravone), Positive Drug Group 2 (Nimodipine)
Methodology:
• The right middle artery of the mice was blocked by suture method, and the suture was removed after blocking for 2h to achieve reperfusion.
• Pharmacodynamics Study: Animals were given the positive drugs by intravenous injection at 0.5h after infarction, and the pharmacodynamic effects of the two positive drugs were investigated.
Inspection indicators
Zea-longa score, Infarct Volume by TTC method
Result-1: Behavioral Scores of Rats
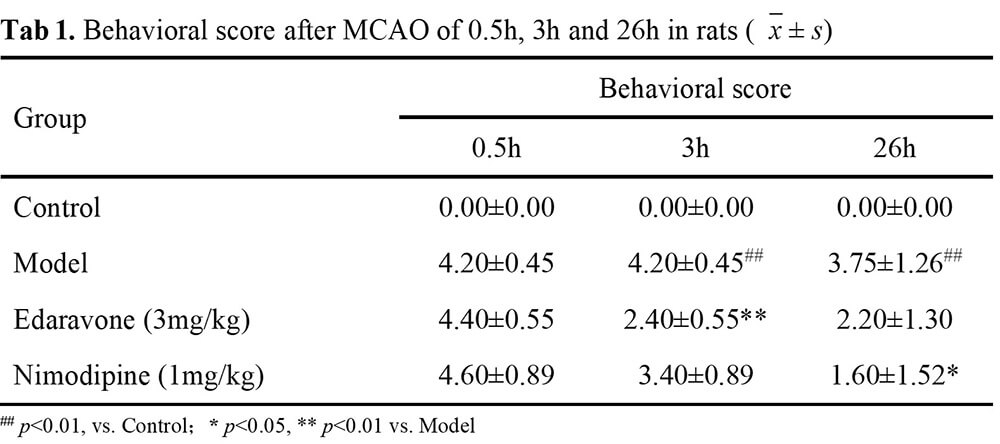
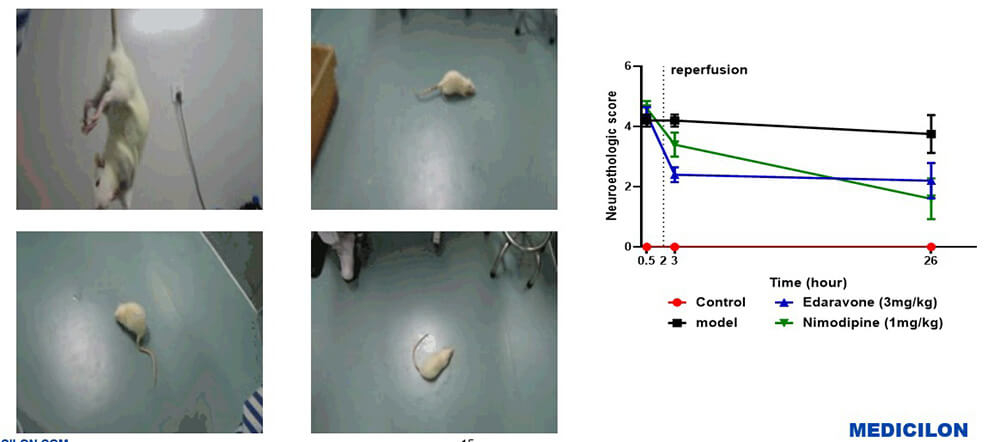
Rat Behavioural Examination (Zea-longa Score and Animal Behaviour)
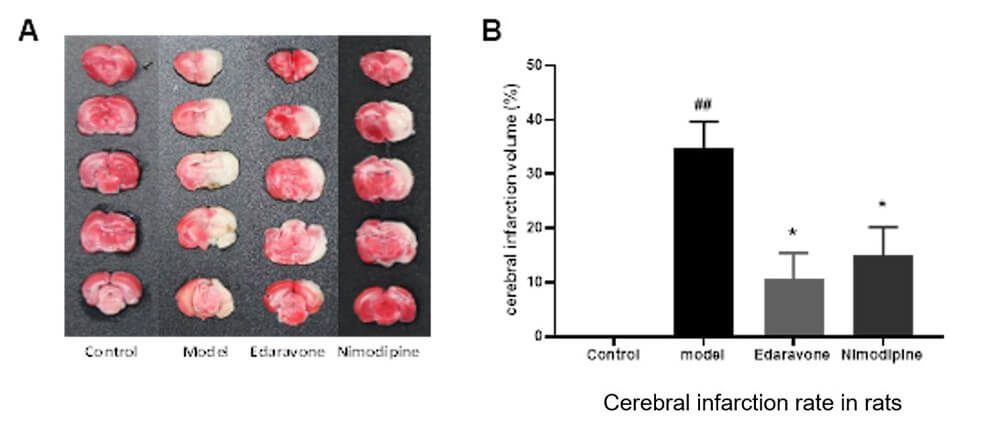
Result-2:TTC Staining of Brain
Cerebral Infarction Volume Investigation (TTC staining and infarct volume ratio)
Other articles you maybe interested:
1. Novel Parkinson's Therapies Possible with New Mouse Model
2. New Player in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis Identified
3. Neuropathic Pain Eased by Novel Light-Based Technique
4. MS Drug Slows Brain Shrinkage by Nearly Half
 관련 실험실
관련 실험실





